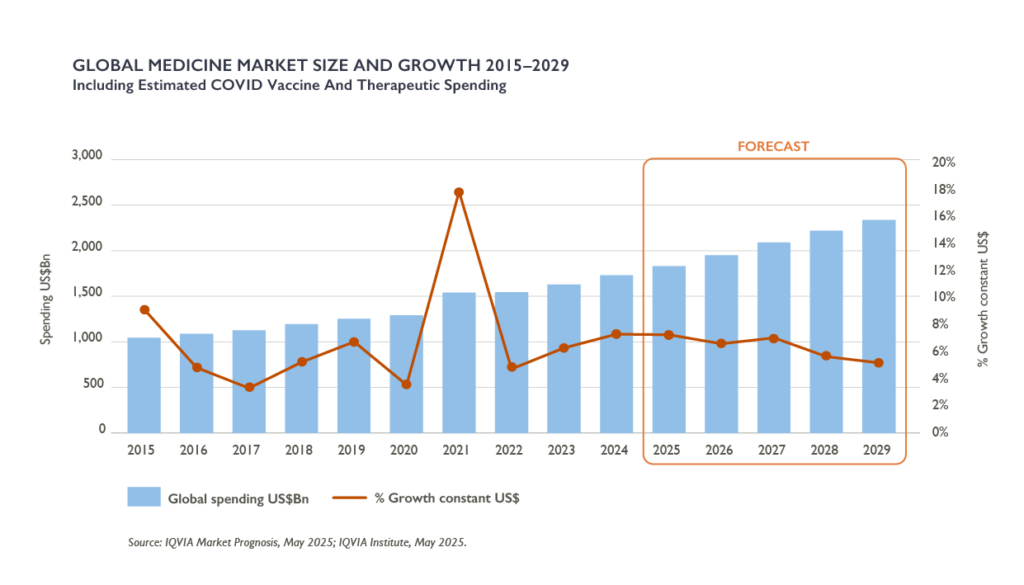
According to IQVIA Institute’s report “The Global Use of Medicines Outlook through 2029”, the global pharmaceutical landscape is entering a transformative phase. By 2029, global medicine spending is projected to reach $2.4 trillion, growing at a 5–8% CAGR. This growth is supported by sustained innovation, balanced by significant losses of exclusivity (LOE) due to patent expiries, especially in small molecules and biologics, regional dynamics, and evolving payer strategies.
Spending trends vary by region, with North America and Europe leading growth, while Japan remains relatively flat due to pricing policies, and China experiences moderate recovery post-pandemic.
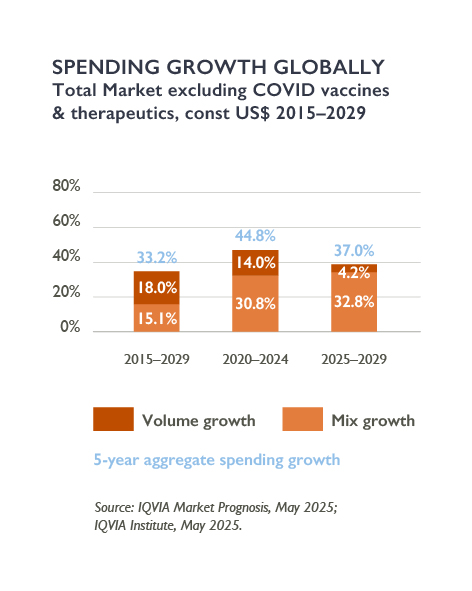
However, the next five years will also be defined by unprecedented patent expiries, intensifying payer cost-containment pressures, and a widening divergence in regional growth trajectories. For C-level leaders, the challenge lies in balancing investment in innovation with navigating structural headwinds.
United States
Growth Outlook: Net spending growth forecasted at 3–6% CAGR, down from 6.8% in the past five years, but absolute spending will rise by $344 billion, $54 billion more than the $290 billion increase over the past five years, driven by protected brands and new launches.
Key Drivers:
Challenges:
Europe (EU4 + UK)
Growth Outlook: European markets anticipate an $85 billion increase in medicine spending by 2029, driven by new and existing brands.
Key Drivers:
Challenges:
Japan
Flat Growth: Spending growth is expected to maintain a consistent -0.5 to 2.5% growth rate over the next five years as annual price cuts offset gains from innovation.
Market Shifts:
China
Gradual Recovery: Growth forecast at 1–4% CAGR, driven by original branded medicines, reaching $190+ Bn by 2029, an increase of $24Bn in the next five years.
Key Drivers:
Challenges:
Latin America
Growth Outlook: Latin America presents a diverse mix of historical and projected market trends, with the largest economies expected to decelerate yet still sustain growth rates above 7% over the forecast period.
Key Dynamics:
Eastern Europe
Highest Growth Outlook: 7–10% CAGR, with spending expected to increase 52% over five years, while volume will increase 2%.
Drivers:
The global medicines market outlook for 2024–2029 presents a complex challenge. While robust growth is expected, the risk environment is becoming more difficult. Projections suggest spending will reach $2.4 trillion by 2029, but the growth patterns will vary significantly across regions and therapeutic areas.
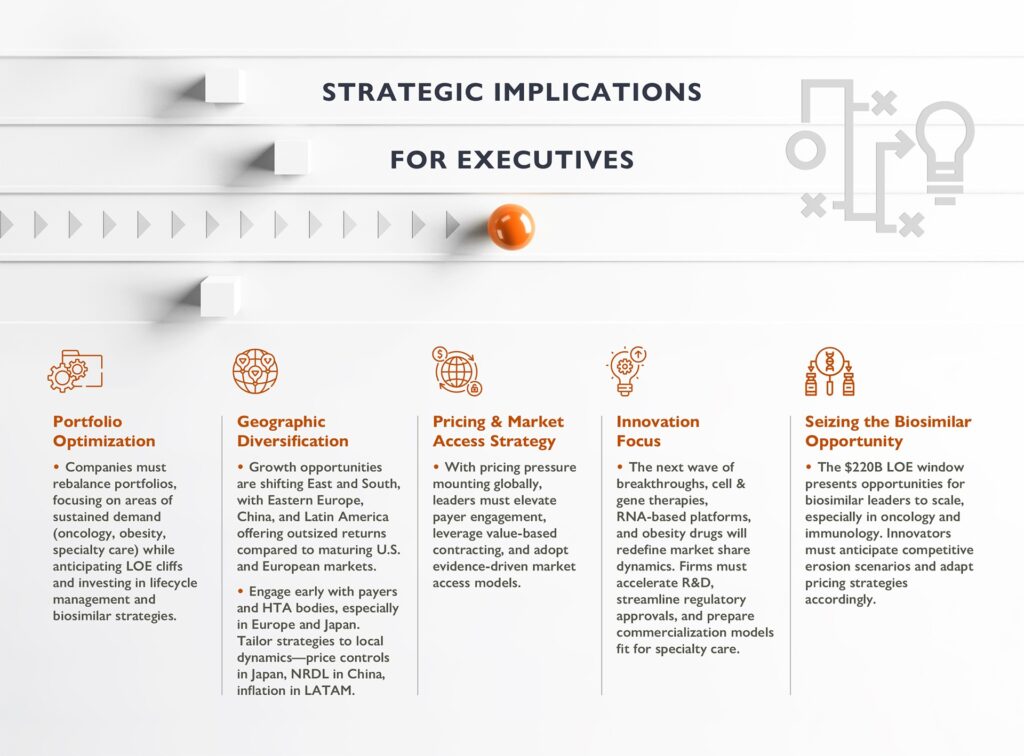
Executives in the sector should focus on several critical priorities:
The leaders who thrive will be those who move with confidence—realigning their portfolios, rethinking market access, and seizing opportunities in both innovation and biosimilars—while staying nimble in the face of constant change.
Source: The Global Use of Medicines Outlook through 2029, IQVIA
20 years of experience in international business development in the pharmaceutical industry. Head of commercial operations and business development for Bristol-Myers Squibb in 16 Latin American countries. Global management consultant. Speaks French and Spanish fluently. Completed nine transactions in global markets in the past three years.